All You Need to Know About Symptoms and Causes of Kidney Stones
Introduction:
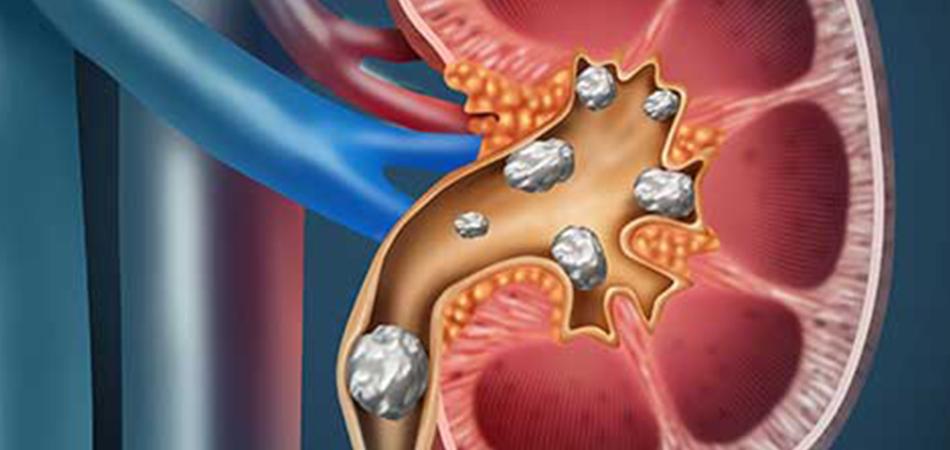
Kidney stones can be painful, and it may feel like something is stuck in your back, or you are constantly feeling the need to urinate. It is very important that you should know the symptoms of kidney stones. If the stone does not come out on its own or if the pain gets worse, you should go to a urologist. Kidney stone symptoms are most common in men and women between the ages of 20 and 50. The main symptoms of kidney stones are intense pain in the lower back or side, vomiting, fever, and blood in the urine.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones:
- Intense Pain:
- One of the hallmark symptoms of kidney stones is severe pain, often referred to as renal colic. This pain typically occurs in the back or side and can radiate to the lower abdomen and groin. The intensity of the pain can fluctuate as the stone moves through the urinary tract.
- Hematuria (Blood in Urine):
- Kidney stones can cause blood to appear in the urine, a condition known as hematuria. The urine may appear pink, red, or brown.
- Frequent Urination:
- Individuals with kidney stones may experience an increased urge to urinate. The urge may be persistent, and small amounts of urine may be passed frequently.
- Painful Urination:
- Pain or a burning sensation during urination can occur as the kidney stone irritates the urinary tract.
- Cloudy or Foul-Smelling Urine:
- The presence of kidney stones can result in changes to the appearance and odor of urine. Cloudiness or an unpleasant smell may be observed.
- Nausea and Vomiting:
- The intense pain associated with kidney stones can lead to nausea and vomiting. Dehydration due to reduced fluid intake can exacerbate these symptoms.
- Fever and Chills:
- In some cases, kidney stones can cause fever and chills, particularly if there is an associated infection.
Causes of Kidney Stones:
- Dehydration:
- Insufficient fluid intake is a primary risk factor for kidney stone formation. When there is a reduced volume of urine, the concentration of minerals and salts in the urine increases, leading to the formation of stones.
- Dietary Factors:
- Certain foods contribute to the formation of kidney stones. Diets high in sodium, animal proteins, and oxalate-rich foods (such as beets, chocolate, and nuts) can increase the risk.
- Calcium Oxalate Stones:
- The most common type of kidney stone is the calcium oxalate stone. These stones form when there is an excess of calcium and oxalate in the urine. Certain medical conditions and high doses of vitamin D can contribute to their development.
- Uric Acid Stones:
- Uric acid stones form when there is an excessive amount of uric acid in the urine. Conditions such as gout, dehydration, and certain genetic factors can lead to the development of these stones.
- Struvite Stones:
- Struvite stones can form in response to urinary tract infections. These stones are composed of magnesium, ammonium, and phosphate. If not addressed promptly, struvite stones can grow large and cause blockages.
- Cystine Stones:
- Cystine stones are rare and result from a genetic disorder that causes an excess of cystine in the urine. Individuals with cystinuria are prone to developing these stones.
- Obstruction of Urinary Tract:
- Any condition that obstructs or impedes the normal flow of urine can contribute to the formation of kidney stones. Examples include an enlarged prostate, kidney tumors, or structural abnormalities in the urinary tract.
- Medical Conditions:
- Certain medical conditions, such as hyperparathyroidism and inflammatory bowel disease, can increase the risk of kidney stone formation. These conditions affect the balance of minerals in the body.
- Family History:
- A family history of kidney stones may increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing stones. Genetic factors can influence the likelihood of stone formation.
Diagnosis and Evaluation:
- Medical History:
- A comprehensive medical history, including information about diet, fluid intake, and family history, is crucial in evaluating the risk factors for kidney stones.
- Physical Examination:
- A physical examination may reveal signs of pain, tenderness, or abnormalities that could be associated with kidney stones.
- Imaging Studies:
- Imaging studies, such as a CT scan, ultrasound, or X-ray, can visualize the size and location of kidney stones. These tests also help determine if there is any obstruction in the urinary tract.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Urinalysis and blood tests can provide information about the composition of the urine and identify any underlying medical conditions contributing to stone formation.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Hydration:
- Staying well-hydrated is crucial for preventing kidney stones. Adequate fluid intake helps dilute the minerals and salts in the urine, reducing the risk of stone formation.
- Dietary Modifications:
- Adjusting the diet to reduce the intake of oxalate-rich foods, limiting sodium, and moderating the consumption of animal proteins can be beneficial in preventing certain types of kidney stones.
- Medications:
- Depending on the type of kidney stones and the underlying causes, medications may be prescribed to alter urine composition, reduce stone formation, or manage associated conditions.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and maintaining a balanced diet, contributes to overall well-being and may help prevent kidney stones.
- Medical Expulsion Therapy:
- In some cases, medications known as alpha-blockers may be prescribed to relax the muscles in the ureter, facilitating the passage of small kidney stones.
- Surgery:
- Surgical intervention may be necessary for large or obstructive kidney stones. Procedures such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), ureteroscopy, or percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PNL) can be employed to remove or break up stones.
Conclusion:
Kidney stones can cause significant pain and discomfort, but with proper understanding of the symptoms, causes, and preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their risk. Regular medical check-ups, a balanced diet, and staying well-hydrated are key components of kidney stone prevention. then you should consult the Best Urologist In Jaipur. Dr Sandeep Nunia is the most reputed Urology doctor in Jaipur and has years of work experience and is the best Urologist in Jaipur for treating ailments such as Laparoscopic treatment, Female Urology, Sexology treatment, Uro Oncology, and Kidney stone treatment.



