Comprehensive Guide to Lung Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Costs in India
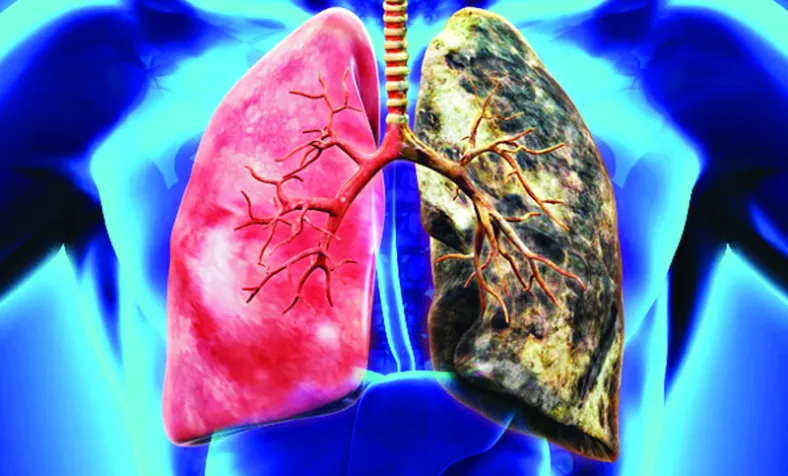
Lung cancer is a critical health issue worldwide and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths. It develops when abnormal cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that can disrupt the lungs’ primary function of oxygenating the body. Often, lung cancer does not show symptoms until it has advanced, making early detection and treatment challenging. This guide explores lung cancer, its types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the costs associated with lung cancer treatment in India.
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is primarily divided into two main categories:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): This type is the most prevalent, accounting for about 85% of lung cancer cases. It includes several subtypes:
- Adenocarcinoma: The most frequent NSCLC subtype, usually found in the lung’s outer regions and more common in non-smokers.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Typically associated with smoking and found in the central part of the lungs near the bronchus.
- Large Cell Carcinoma: Can occur in any lung part and tends to grow and spread quickly, complicating treatment.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): Representing about 15% of lung cancers, SCLC is more aggressive than NSCLC and strongly linked to smoking. It tends to spread rapidly to other body parts.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of lung cancer is smoking, responsible for approximately 85% of cases. Both active smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke significantly increase the risk. Other contributing factors include:
- Radon Gas Exposure: Radon, a naturally occurring radioactive gas, can accumulate in buildings. Long-term exposure to high radon levels raises lung cancer risk.
- Occupational Hazards: Jobs involving exposure to carcinogens like asbestos, arsenic, and diesel exhaust can increase lung cancer risk.
- Air Pollution: Long-term exposure to polluted air, particularly in urban areas, contributes to lung cancer risk.
- Genetics: A family history of lung cancer may indicate a genetic predisposition, elevating individual risk.
- Lung Disease History: Conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can increase lung cancer susceptibility.
Symptoms
Lung cancer symptoms often do not manifest until the disease is advanced. Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent worsening cough
- Chest pain exacerbated by deep breathing, coughing, or laughing
- Hoarseness
- Unexplained weight loss and loss of appetite
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or weakness
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum
- Frequent lung infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia
Diagnosis
Diagnosing lung cancer involves multiple tests and procedures. Initially, a medical history review and physical examination are conducted, followed by imaging tests like chest X-rays and CT scans to detect lung abnormalities. If suspicious areas are found, further diagnostics may include:
- Sputum Cytology: Examining mucus under a microscope to identify cancer cells.
- Biopsy: Extracting a tissue sample for examination through methods like bronchoscopy, needle biopsy, or surgical biopsy.
- Mediastinoscopy: A procedure to examine the chest’s central part and obtain tissue samples.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: An advanced imaging test to detect cancer spread.
Treatment Options
Lung cancer treatment varies based on the cancer type, stage, and patient health. Common treatments include:
- Surgery: Removing part or all of the lung affected by cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells, used alone or with other treatments.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells, often used for cancer that has spread.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs targeting specific genetic changes in cancer cells, effective for certain mutations.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the immune system to fight cancer, used for specific lung cancer types.
- Palliative Care: Focuses on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life for advanced-stage patients.
Lung Cancer Treatment Cost in India
India offers significantly lower lung cancer treatment cost compared to many Western countries, making it a preferred destination for medical tourists. Treatment costs can vary widely based on treatment type, cancer stage, hospital, and city.
Factors Influencing Costs:
- Treatment Type: Surgical procedures, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy each have different cost structures. Surgery may cost between INR 2,00,000 and INR 4,00,000 (USD 2,500 to USD 5,000), while chemotherapy cycles range from INR 50,000 to INR 1,50,000 (USD 625 to USD 1,875) per cycle.
- Hospital and Location: Costs vary by hospital and region. Major cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore typically have higher treatment costs compared to smaller cities. Top-tier hospitals with advanced facilities may charge more than regional hospitals.
- Treatment Duration: Longer or combination treatment plans increase total expenses.
- Diagnostic Tests: Frequent diagnostic tests such as CT scans, PET scans, and biopsies add to the overall cost, ranging from INR 5,000 to INR 20,000 (USD 62 to USD 250) per test.
- Hospital Stay and Post-Treatment Care: Length of hospital stay and the need for post-treatment care and medications also affect costs.
Estimated Treatment Costs:
- Surgery: INR 2,00,000 to INR 4,00,000 (USD 2,500 to USD 5,000)
- Chemotherapy: INR 50,000 to INR 1,50,000 (USD 625 to USD 1,875) per cycle
- Radiation Therapy: INR 1,50,000 to INR 3,00,000 (USD 1,875 to USD 3,750)
- Targeted Therapy: INR 1,00,000 to INR 2,50,000 (USD 1,250 to USD 3,125) per month
- Immunotherapy: INR 2,00,000 to INR 5,00,000 (USD 2,500 to USD 6,250) per month
These costs are estimates and can vary based on individual treatment plans and patient needs. Patients should discuss financial aspects with their healthcare providers.
Conclusion
Lung cancer is a significant health challenge globally, but advances in medical technology and treatment strategies are improving outcomes. Early detection through regular screening, especially for high-risk individuals, is crucial for effective management.
In India, the relatively affordable cost of lung cancer treatment compared to other countries makes it a viable option for local and international patients. By understanding lung cancer, its treatment options, and associated costs, patients and their families can make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of this challenging disease.