Dental Procedures for Treating Gum Disease
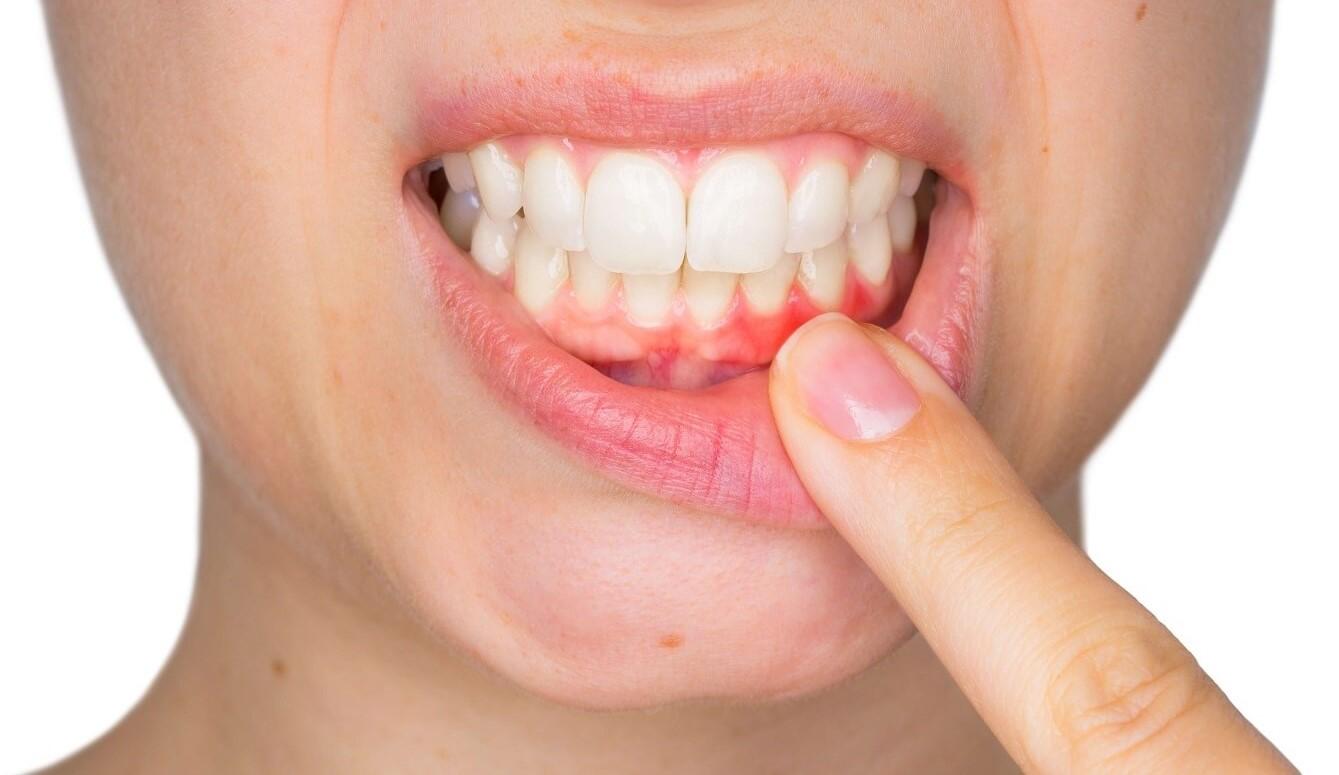
Are your gums giving you a reason to frown? Gum disease is a common oral health issue that can cause discomfort, pain, and even tooth loss if left untreated. But fear not! In this blog post, we’ll explore the ins and outs of gum disease treatment. From understanding the causes and symptoms to exploring non-surgical and surgical procedures, we’ve got you covered. So sit back, relax (but don’t forget to brush!), as we dive into the world of dental procedures for treating gum disease. Together, let’s reclaim those healthy smiles!
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and surrounding tissues in the mouth. It occurs when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up on the teeth and along the gumline. If left untreated, gum disease can progress from mild inflammation (gingivitis) to more severe infection (periodontitis).
Causes and Symptoms of Gum Disease
The primary cause of gum disease is poor oral hygiene. When we neglect our dental care routine – brushing twice a day and flossing regularly – plaque accumulates and hardens into tartar, which irritates the gums. Other factors such as smoking, hormonal changes in women, genetic predisposition, certain medications can also contribute to its development.
So how do you know if you have gum disease? Look out for symptoms like redness or swelling of the gums, bleeding while brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath or taste in your mouth. In advanced stages of periodontitis, you may experience loose teeth or even tooth loss.
Prevention of Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease starts with maintaining good oral hygiene habits. Brush your teeth thoroughly using fluoride toothpaste at least twice daily for two minutes each time. Don’t forget to clean between your teeth with floss or interdental brushes daily.
Regular visits to your dentist are crucial too! They will perform professional cleanings and check for any signs of gum problems before they worsen.
Stay tuned as we discuss non-surgical treatments like scaling & root planing and surgical procedures for advanced cases of gum disease in our upcoming sections!
Causes and Symptoms of Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the gums and surrounding tissues. While poor oral hygiene is often a major contributor to gum disease, there are several other factors that can increase your risk.
One of the main causes of gum disease is plaque buildup. When bacteria in the mouth combine with food particles and saliva, they form a sticky film called plaque. If plaque isn’t removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar and irritate the gums.
Other potential causes include hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or menopause), certain medications that reduce saliva flow, smoking or tobacco use, genetic predisposition, and systemic diseases like diabetes.
Recognizing the symptoms of gum disease is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common signs include redness or swelling of the gums, tenderness or bleeding while brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath (halitosis), receding gums, loose teeth, changes in bite alignment, and even abscesses.
If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect you may have gum disease due to one or more risk factors mentioned above – schedule an appointment with your dentist promptly. Early intervention can prevent further damage to your gums and teeth!
Prevention of Gum Disease
Prevention is always better than cure, and this holds true for gum disease as well. By taking certain precautions, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing this common dental issue.
Maintaining proper oral hygiene is key. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a soft toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Don’t forget to clean the areas between your teeth using dental floss or interdental brushes.
In addition to regular brushing and flossing, it’s important to visit your dentist for routine check-ups and cleanings. These appointments allow your dentist to detect any signs of gum disease early on and provide necessary treatment.
A healthy lifestyle also plays a crucial role in preventing gum disease. Avoid tobacco products as they increase the risk of gum problems. Additionally, eat a balanced diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables while limiting sugary snacks and beverages.
Managing stress levels can contribute to overall oral health. Studies have shown that stress weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections such as gum disease.
By following these preventive measures consistently, you can help keep gum disease at bay and maintain optimal oral health!
Non-surgical Treatments for Gum Disease
Non-surgical treatments for gum disease can be a highly effective way to combat the early stages of this common oral health issue. When caught in its initial phases, gum disease can often be managed without the need for invasive procedures.
One non-surgical treatment option is professional dental cleaning. During this procedure, known as scaling and root planing, your dentist will carefully remove plaque and tartar buildup from both above and below the gumline. This thorough cleaning helps to eliminate bacteria that contribute to gum disease.
Another non-surgical approach is the use of antibiotics. These medications can be prescribed by your dentist or periodontist to help control bacterial infections in the gums. Antibiotics may be administered orally or applied directly to the affected areas using gels or mouth rinses.
In some cases, laser therapy may also be recommended as a non-surgical treatment for gum disease. This technique involves using a specialized dental laser to target and eliminate bacteria while promoting healing in the gums.
Regular follow-up appointments with your dentist are essential after undergoing any non-surgical treatments for gum disease. These visits allow your oral health care provider to monitor your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
By taking advantage of these non-invasive options, you can effectively manage gum disease before it progresses into more severe stages requiring surgical intervention. However, it’s important to remember that prevention is always better than cure when it comes to maintaining healthy gums in the long term!
Surgical Procedures for Advanced Gum Disease
When non-surgical treatments fail to effectively treat advanced gum disease, surgical procedures may be necessary. These procedures are typically performed by a periodontist, a dental specialist who focuses on treating gum diseases.
One common surgical procedure for advanced gum disease is called flap surgery or pocket reduction surgery. During this procedure, the periodontist lifts back the gums and removes tartar buildup from deep pockets around the teeth. The gums are then repositioned tightly around the teeth to prevent further bacteria growth.
Another surgical option is bone grafting, which involves replacing damaged bone tissue with either natural or synthetic materials. This helps regenerate lost bone and provides a stable foundation for the teeth.
In some cases, soft tissue grafts may be required to cover exposed tooth roots or increase gum tissue thickness. This can help reduce sensitivity and improve overall aesthetics.
For severe cases of gum disease that have led to significant bone loss, guided tissue regeneration may be recommended. This procedure involves placing special membranes between the gum tissue and tooth root to encourage new bone growth.
It’s important to note that while these surgical procedures can effectively treat advanced gum disease, proper aftercare is crucial for successful healing and prevention of future infections. Regular maintenance visits with your dentist or periodontist will also be necessary to monitor your oral health progress.
Remember, early detection and treatment of gum disease is always preferable over reaching an advanced stage where surgery becomes necessary. So make sure you practice good oral hygiene habits at home and visit your dentist regularly for check-ups!
Recovery and Aftercare Tips
After undergoing dental procedures for gum disease, it is crucial to take proper care of your gums to ensure a smooth and speedy recovery. Here are some essential tips for post-treatment aftercare:
1. Follow the dentist’s instructions: Your dentist will provide you with specific guidelines on how to care for your gums after treatment. It is important to follow these instructions diligently.
2. Maintain good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth gently twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush. Don’t forget to clean along the gumline carefully.
3. Use antimicrobial mouthwash: Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash recommended by your dentist daily, especially in the first few weeks after treatment.
4. Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption: Smoking can hinder the healing process and increase the risk of complications, while alcohol can irritate sensitive gums.
5. Adopt a healthy diet: Include nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains in your diet as they promote healing.
6. Be cautious with hot or cold food/drinks: Sensitive gums may be more susceptible to discomfort from extreme temperatures; avoid consuming extremely hot or cold items until fully recovered.
7. Attend regular check-ups: Schedule follow-up appointments with your dentist as advised for professional monitoring of your gum health.
By following these recovery and aftercare tips, you can help facilitate optimal healing and maintain long-term gum health.
Maintaining Healthy Gums for the Long Term
Now that you have learned about various dental procedures for treating gum disease, it is important to focus on maintaining healthy gums for the long term. Prevention and regular oral hygiene habits are key in ensuring your gums stay healthy. Here are some tips to help you maintain optimal gum health:
1. Brush and floss regularly: Make sure to brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Flossing should be done once daily to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth.
2. Use mouthwash: Incorporating an antibacterial mouthwash into your daily routine can help reduce bacteria in the mouth and prevent gum disease.
3. Eat a balanced diet: A nutritious diet plays a significant role in your overall oral health. Limit sugary snacks and beverages as they can contribute to bacterial growth in the mouth.
4. Quit smoking: Smoking not only stains your teeth but also increases the risk of developing gum disease. If you smoke, consider quitting or seeking support to help kick this habit.
5. Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups are crucial for detecting any early signs of gum disease or other oral health issues before they become more severe.
6. Professional cleanings: Schedule professional cleanings with your dentist or dental hygienist every six months or as recommended by them.
7. Avoid excessive force when brushing: Aggressive brushing can damage delicate gum tissue over time, so make sure to use gentle circular motions when brushing.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease and maintain optimal oral health in the long run!
Remember, early detection and treatment are essential for successful management of gum disease, so if you notice any symptoms such as bleeding gums or persistent bad breath, don’t hesitate to consult with your dentist promptly!



